Tinnitus – Causes, Symptoms, Precautions, and More
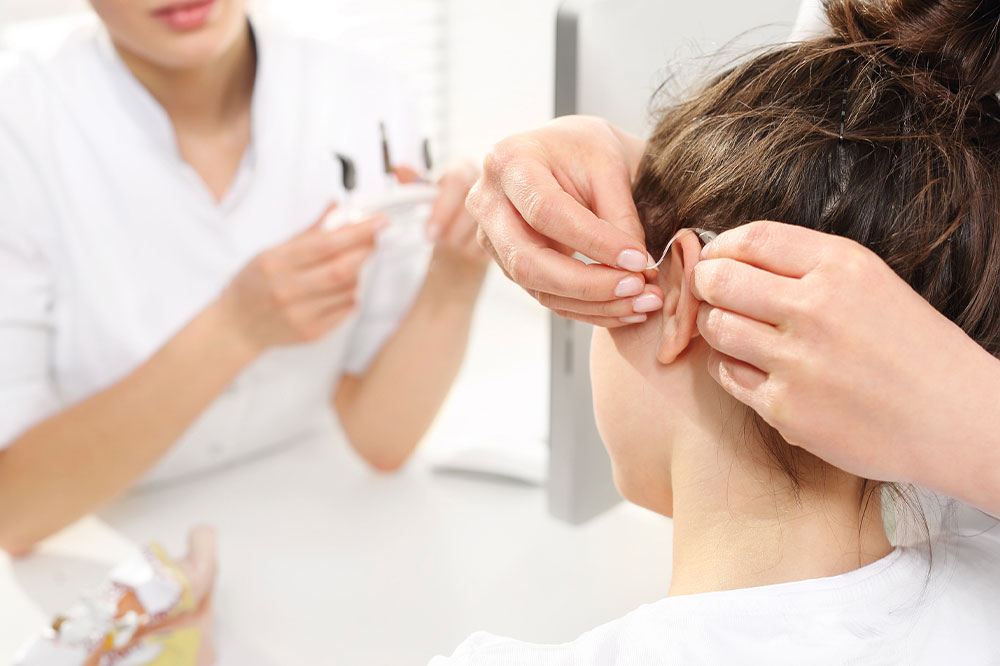
Experiencing constant noise in the head, such as ringing in the ears, can be annoying. The noise is continuous or intermittent, pulsating, shrill, and varying in loudness. It can occur due to various causes, from exposure to loud noise to underlying health conditions. Also known as tinnitus, this ringing in the ears affects nearly 50 million people in the country. Here’s all you need to know about tinnitus: causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and precautions.
Causes of tinnitus
Prolonged exposure to loud noises
This is one of the most common causes of tinnitus. Nearly 90 percent of the people who experience tinnitus have hearing loss induced by noise. The repeated exposure to loud sounds can cause damage to the sound-sensitive cells of the inner ear. This damage can often be permanent. Pilots, carpenters, street-repair workers, landscapers, rock musicians, and others who have to work in a constantly noisy environment are generally at risk. Sometimes, tinnitus is also caused by a single exposure to a sudden, extremely loud noise.
Blockages in the ear
If there is any blockage in the ear canal, it can cause tinnitus. The blockage can be due to an ear infection or buildup of wax. Sometimes, the development of a benign tumor of the auditory nerve can also cause ringing in the ears.
Natural aging process
Tinnitus is quite common among seniors. Aging can cause a deterioration of several parts of the ear, including the cochlea. As a result, there can be hearing loss accompanied by continuous or intermittent ringing in the ears.
Health conditions
Certain health conditions related to the ear can also cause tinnitus. For example, Meniere’s disease affects the inner parts of the ear, and otosclerosis stiffens the small bones in the middle ear.
Underlying health issues
Some people experience tinnitus due to underlying health issues such as cardiovascular disease, high blood pressure, anemia, circulatory problems, underactive thyroid gland, allergies, diabetes, and autoimmune disease.
Problems in the head or neck
Problems related to the jaw or neck, like temporomandibular joint (TMJ) syndrome or injuries to the head, can also cause tinnitus.
Symptoms
Apart from the constant ringing in the ears, tinnitus doesn’t have any specific symptoms. It is generally experienced as hearing phantom noises in your ears, such as buzzing, roaring, clicking, hissing, and humming. The tinnitus that is experienced is called subjective, as it can only be heard by the person who has it. The pitch of the noise will vary from a low roar to a high squeal. It can occur in one or both ears. In some cases, the nose is too loud and causes interference in carrying out routine daily activities.
In some cases, people experience tinnitus as a whooshing or rhythmic pulsing sound. The sound is often heard in sync with the heartbeats. This is known as pulsatile tinnitus. This is an objective type of tinnitus that can be heard by others, particularly during an ear examination.
Diagnosis
It is not easy to get a diagnosis of tinnitus. The reason for this is that only the person experiencing tinnitus can hear it, unless it is objective tinnitus, which is quite rare. In most cases when tinnitus occurs due to hearing loss, a hearing test is used for diagnosis. In this, a primary care physician or an audiologist will examine the ear and do a hearing test.
During the test, a sound is transmitted to each ear through headphones. The person undergoing the test has to acknowledge when they hear each sound. Hearing loss can be diagnosed by comparing what the person can hear with what people of the same age and gender sex can hear. In some cases, doctors also recommend additional tests, such as MRI or CT scan, to check for damage or irregularities. These tests are generally done to ascertain the cause of tinnitus.
Treatment
Since tinnitus is a symptom of other health conditions, the only way to treat it is by managing any underlying health conditions causing it. Some common treatments are as follows.
Removing any excess earwax from the ear canals.
Treating any blood vessel issues that are causing the ringing sound in the ears.
Using noise-canceling machines to dull the buzzing or ringing sounds.
Inserting a masking device in the ear to mask the tinnitus.
Using a hearing aid if tinnitus is occurring due to hearing loss.
Undergoing cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) or acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT) to learn how to pay less attention to ringing and buzzing sounds in the ear.
Doing biofeedback therapy can help to manage stress and deal with tinnitus that is distracting a person from doing their routine daily activities.
Precautions for preventing tinnitus
One of the best ways to prevent tinnitus is by protecting one’s hearing. Individuals can list all their daily activities to help determine whether any activity is exposing the ears to loud sounds and noises. Here are a few possible activities that can affect hearing, leading to tinnitus.
At the workplace
Those who work in the fields of landscaping, construction, assembly line, or around heavy and loud machinery are continuously exposed to extremely high decibels. In such cases, ears should be protected by wearing gears such as earplugs or noise-canceling safety ear muffs.
At the gym
A lot of gyms often play extremely loud music to keep people moving and exercising. Although this is done for motivational purposes, it can harm the ears. Wearing earplugs and noise-canceling headphones can be useful in such situations. Also, working out away from the noise source is recommended.
At concerts and movie theaters
Surround sound systems generate extremely loud sounds at the movie theater and concerts. Since it takes just one sudden exposure to loud noise to bring about tinnitus, it’s best to use earplugs as precautionary measures in such places.
Use earphones with low volume
Listening to music, podcasts, or audiobooks through earphones at a high volume should be avoided.


